Chapter: Nervous System and Sense Organs
Nervous system and sense organs control the entire body. It is expected that the student should be aware of the functioning of these systems in a cursory way.
For success in the entrance tests following points are important to retain.
- The nervous system controls all other systems of the body.
- The nervous system is made up of the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves.
- Nerves are like wires that link the body organs and muscles to the brain and spinal cord.
- Nerves are made up of neurons or nerve cells.
- Nerve cells have special thread-like parts called filters.
- Sensory Nerves: The nerves which are connected to the sense organs and carry the messages from sense organs to the brain or spinal cord are known as sensory nerves.
- Motor Nerves: The nerves which carry orders from the brain or the spinal cord to the muscles and glands are known as motor nerves.
- The message by the motor nerves results in the movement of the muscles or secretion by glands.
- Mixed Nerves: These nerves do both the functions i.e. they carry messages to the brain as well as carry orders from the brain.
- There are some actions which are automatic and we do not have to think before the act. These actions are called as reflex actions.
- Some of the human reflexes are coughing, sneezing, blinking and jumping when frightened and watering of mouth on seeing some tasty food.
- The brain is the main control centre of the body.
- The brain is divided into left and right halves.
- The brain attains its full size by the time a person is six years old and it weighs about 1.4 kg.
- The brain is a very delicate organ and therefore it is well protected, located inside a hard brain box or skull.
- Between the skull and the brain is present cerebrospinal fluid which absorbs the shocks, bumps and jerks.
- The brain needs plenty of food and oxygen.
- The brain uses about 1/4th of all the oxygen used by the body.
- The brain has three main parts the cerebrum, the cerebellum and the brain stem or medulla.
- The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and makes about 90% of the brain tissues.
- The cerebrum controls speech, memory and intelligence.
- Cerebellum remains effective while running, riding a bicycle and also to keep your body balanced.
- The brain stem connects the brain to the spinal cord.
- The medulla controls many vital functions such as breathing and blood circulation.
- The eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin are considered as the important sense organs of the human body.
Eyes
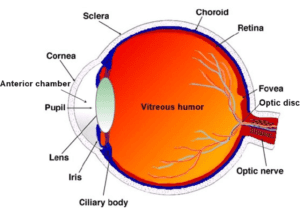
- Eyelids and eyelashes help to keep dust and dirt out of our eyes.
- The light coming from objects passes through the cornea.
- Then it goes through an opening: the pupil.
- The iris provides colour to the eyes.
- The iris controls the amount of light entering into our eyes by changing the size of the pupil.
- Image is formed on the screen of our eyes called the retina.
- The iris closes down in bright light and opens or widens in dim light.
- The optic nerves carry the messages from the eyes to the brain.
Care of the Eyes
- Wash and clean your eyes regularly with cold water.
- Do not read in dim or very bright light.
- Do not read in a moving vehicle and while lying down.
- Stay away at least six feet while watching T.V.
- Never rub your eyes with dirty hands.
Ears
- The ear is the sense organ which helps us to hear.
- The outer part of the ear helps in collecting sound.
- Our ears should be protected from the hard blow and loud sound.
Care for Ears
- Do not let water enter the ears.
- Never try to clean ears with a hairpin, toothpick or matchstick or any sharp object.
- consult a doctor in case of any ear ache.
Nose
- The nose is the sensory organ which detects odour.
- The nose has nerve cells where a chemical reaction occurs and the message is sent to the brain.
Care of Nose
- We should regularly clean our nose with water.
- We should never put a finger in our nose.
- Use nasal drops or inhale steam to clear a blocked nose.
Tongue
- The tongue is a sense organ which detects the taste of our food.
- There are four types of tastes: sweet, salty, sour and bitter.
- The tongue also has receptors for heat, cold, pain and texture.
Skin
- The skin forms a protective covering over our body.
- The five sensations that we can feel through our skin are touch, heat or cold, pressure, pain and tickling.
- Some of our waste water and salts are also removed from our body in the form of sweat.
Care for Skin
- We should always keep our skin clean.
- We should avoid wearing clothes used by others as we may get skin diseases.
- We must always wear clean clothes.
- We should take a bath to keep our skin healthy and clean.