Number System
Roman Numerals
Points to Remember:
- Repetition Rule:
- If any Roman numerals are repeated, their values are added.
For example,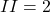 ,
, 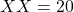 .
.
- If any Roman numerals are repeated, their values are added.
- Subtraction Rule:
- When a smaller numeral is placed before a larger numeral, it is subtracted from the larger numeral.
For example,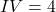 (5 – 1),
(5 – 1), 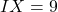 (10 – 1).
(10 – 1).
- When a smaller numeral is placed before a larger numeral, it is subtracted from the larger numeral.
- Addition Rule:
- When a smaller numeral is placed after a larger numeral, it is added to the larger numeral.
For example,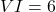 (5 + 1),
(5 + 1), 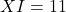 (10 + 1).
(10 + 1).
- When a smaller numeral is placed after a larger numeral, it is added to the larger numeral.
- Placement Rule:
- When a smaller numeral is placed between two larger numerals, it is always subtracted from the larger numeral immediately following it.
For example,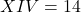 (10 + 5 – 1).
(10 + 5 – 1).
- When a smaller numeral is placed between two larger numerals, it is always subtracted from the larger numeral immediately following it.
Examples:
- Addition:
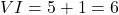
- Subtraction:
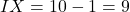
- Complex Examples:
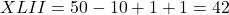
Whole Numbers
Natural Numbers:
- Counting numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, etc.) are called natural numbers.
Whole Numbers:
- All natural numbers together with ‘0’ (zero) are called whole numbers.
Thus,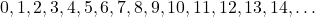 are whole numbers.
are whole numbers. - Every natural number is a whole number, but ‘0’ (zero) is a whole number that is not a natural number.
Successor of a Whole Number:
- If we add 1 to a whole number, the resulting number is called its successor. For example, the successor of 0 is 1, the successor of 1 is 2, the successor of 12 is 13, and so on. Every whole number has its successor.
Predecessor of a Whole Number:
- One less than a given whole number (other than 0) is called its predecessor. For example, the predecessor of 1 is 0, the predecessor of 2 is 1, the predecessor of 10 is 9, and so on.
- The whole number 0 does not have a predecessor.
- Every whole number other than 0 has a predecessor.
Examples:
- Write the successor and predecessor of:
- 1000
- 1005399
- 999999
Solution:
- The successor of 1000 =
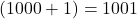 .
. - The predecessor of 1000 =
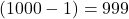 .
. - The successor of 1005399 =
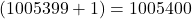 .
. - The predecessor of 1005399 =
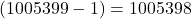 .
. - The successor of 999999 =
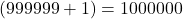 .
. - The predecessor of 999999 =
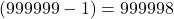 .
.
Properties of Whole Numbers
- Closure Property:
- Whole numbers are closed under addition and multiplication.
For example,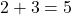 and
and 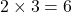 are whole numbers.
are whole numbers.
- Whole numbers are closed under addition and multiplication.
- Commutative Property:
- Whole numbers are commutative under addition and multiplication.
For example,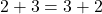 and
and 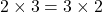 .
.
- Whole numbers are commutative under addition and multiplication.
- Associative Property:
- Whole numbers are associative under addition and multiplication.
For example,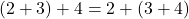 and
and 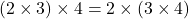 .
.
- Whole numbers are associative under addition and multiplication.
- Distributive Property:
- Multiplication is distributive over addition for whole numbers.
For example,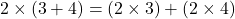 .
.
- Multiplication is distributive over addition for whole numbers.
Simplification
Order of Operations:
- In a simplification sum consisting of the operations
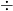 ,
, 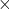 ,
, 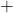 , and
, and  , first do the operations in the order of BODMAS:
, first do the operations in the order of BODMAS:
Examples:
- Without Brackets:
- Simplify:
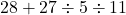
- Solution:
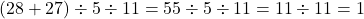
- Simplify:
- With Brackets:
- Simplify:
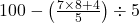
- Solution:
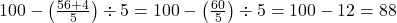
- Simplify: