Identification of Tenses: Key 4 Steps
Introduction to Identification of Tenses
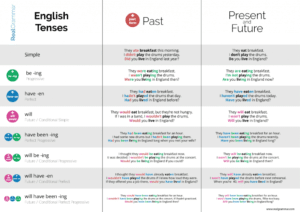
1. Present Tenses
a. Simple Present
- Structure: Subject + base form of the verb (add ‘s’ or ‘es’ for third person singular)
- Usage: General truths, habitual actions, and scheduled events.
- Example: She reads books.
b. Present Continuous
- Structure: Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing
- Usage: Actions happening at the moment of speaking, ongoing actions, and future plans.
- Example: She is reading a book.
c. Present Perfect
- Structure: Subject + has/have + past participle of the verb
- Usage: Actions that happened at an unspecified time or have relevance to the present moment.
- Example: She has read that book.
d. Present Perfect Continuous
- Structure: Subject + has/have been + verb-ing
- Usage: Actions that started in the past and are still continuing or have recently stopped.
- Example: She has been reading for two hours.
2. Past Tenses
a. Simple Past
- Structure: Subject + past form of the verb
- Usage: Actions completed at a specific time in the past.
- Example: She read a book yesterday.
b. Past Continuous
- Structure: Subject + was/were + verb-ing
- Usage: Actions that were ongoing at a specific time in the past.
- Example: She was reading a book at 8 PM.
c. Past Perfect
- Structure: Subject + had + past participle of the verb
- Usage: Actions that were completed before another action in the past.
- Example: She had read the book before the meeting started.
d. Past Perfect Continuous
- Structure: Subject + had been + verb-ing
- Usage: Actions that were ongoing up to a certain point in the past.
- Example: She had been reading for two hours before he arrived.
3. Future Tenses
a. Simple Future
- Structure: Subject + will/shall + base form of the verb
- Usage: Actions that will happen in the future.
- Example: She will read a book.
b. Future Continuous
- Structure: Subject + will be + verb-ing
- Usage: Actions that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future.
- Example: She will be reading a book at 8 PM.
c. Future Perfect
- Structure: Subject + will have + past participle of the verb
- Usage: Actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future.
- Example: She will have read the book by tomorrow.
d. Future Perfect Continuous
- Structure: Subject + will have been + verb-ing
- Usage: Actions that will be ongoing up to a certain point in the future.
- Example: She will have been reading for two hours by the time you arrive.
Identifying Tenses in Sentences
To identify the tense in a sentence, follow these steps:
- Look for Time Indicators: Words like “yesterday,” “tomorrow,” “now,” etc., can provide clues.
- Examine the Verb Forms: Identify the base form, past form, past participle, and present participle.
- Check Auxiliary Verbs: Words like “is,” “are,” “was,” “were,” “has,” “have,” “had,” “will,” etc., help determine the tense.
- Understand the Context: The context of the sentence can give additional hints about the tense.
Further Reading: Detailed Lesson on Tenses
External Resources: https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/verb-tenses.html